Treatments
as well as the intensive care after the surgery, are particularly important.

My medical and surgical emphases:
Hip
Conventional and minimal invasive Hip Joint Replacement
Hip Endoprostheses revisions
Joint preservation and corrective osteotomy
Using the minimal invasive techniques a particularly fast postoperative rehabilitation can be achieved through highest precision and careful handling of the soft tissues. Approved implants can be used with the appropriate modification of the technique and experience of the surgeon. This results in the desired combination of full weight bearing of the joint on the first post-operative day without limping, no need of a partial support with forearm crutches, without endangering long-term results and, in addition, produces a considerably shorter scar which is remarkable for the patient. Furthermore the complication rate on post-operative dislocation is lower, as well as post-operative limping or the occurrence of disturbances in wound healing and hematoma. The blood loss is significantly reduced, so that only in individual cases postoperative blood transfusion is needed.
At the orthopedic department of the EKH Vienna the minimally invasive implantation of hip endoprostheses has already become standard. We started using the anterolateral approach in the supine position in 2004 and have released publications on this technique several times. We are also holding regular workshops for colleagues from all over the world who want to practice this technique.
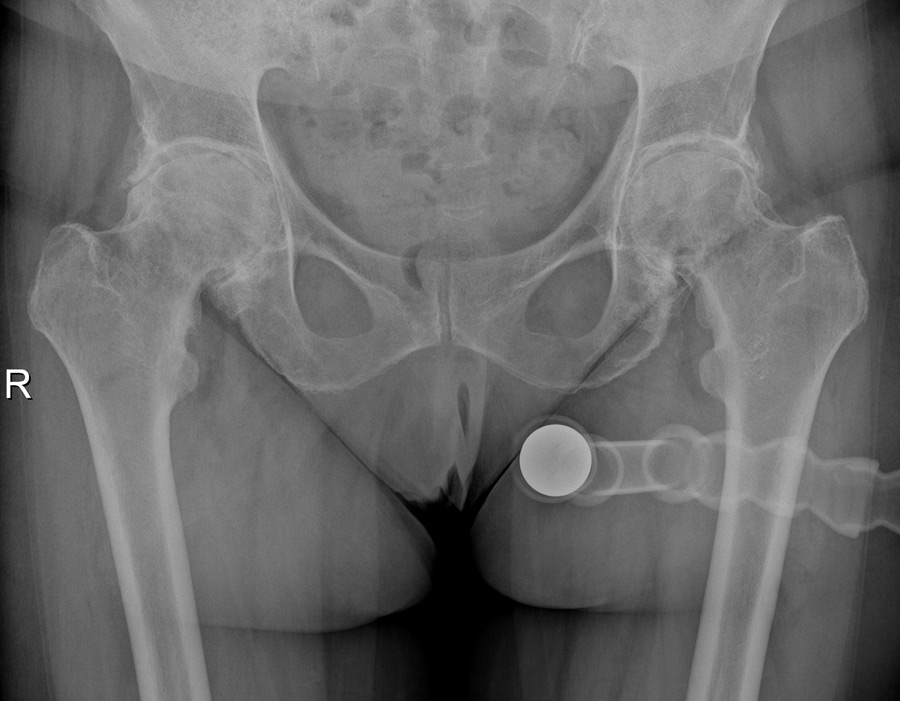
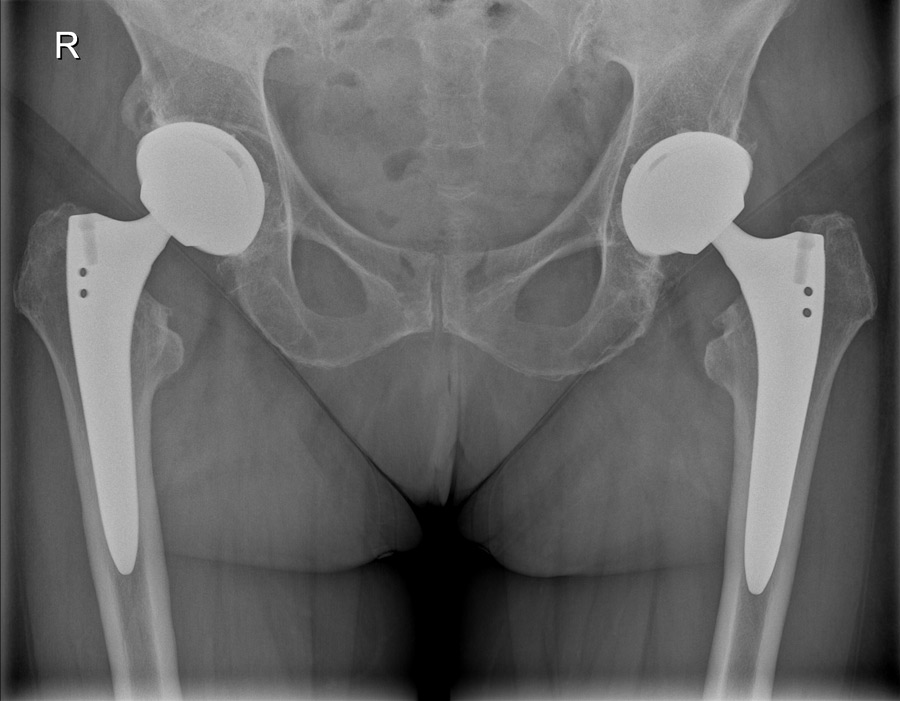
Status before / after total hip replacement on both sides:
Knee
Artificial knee joints
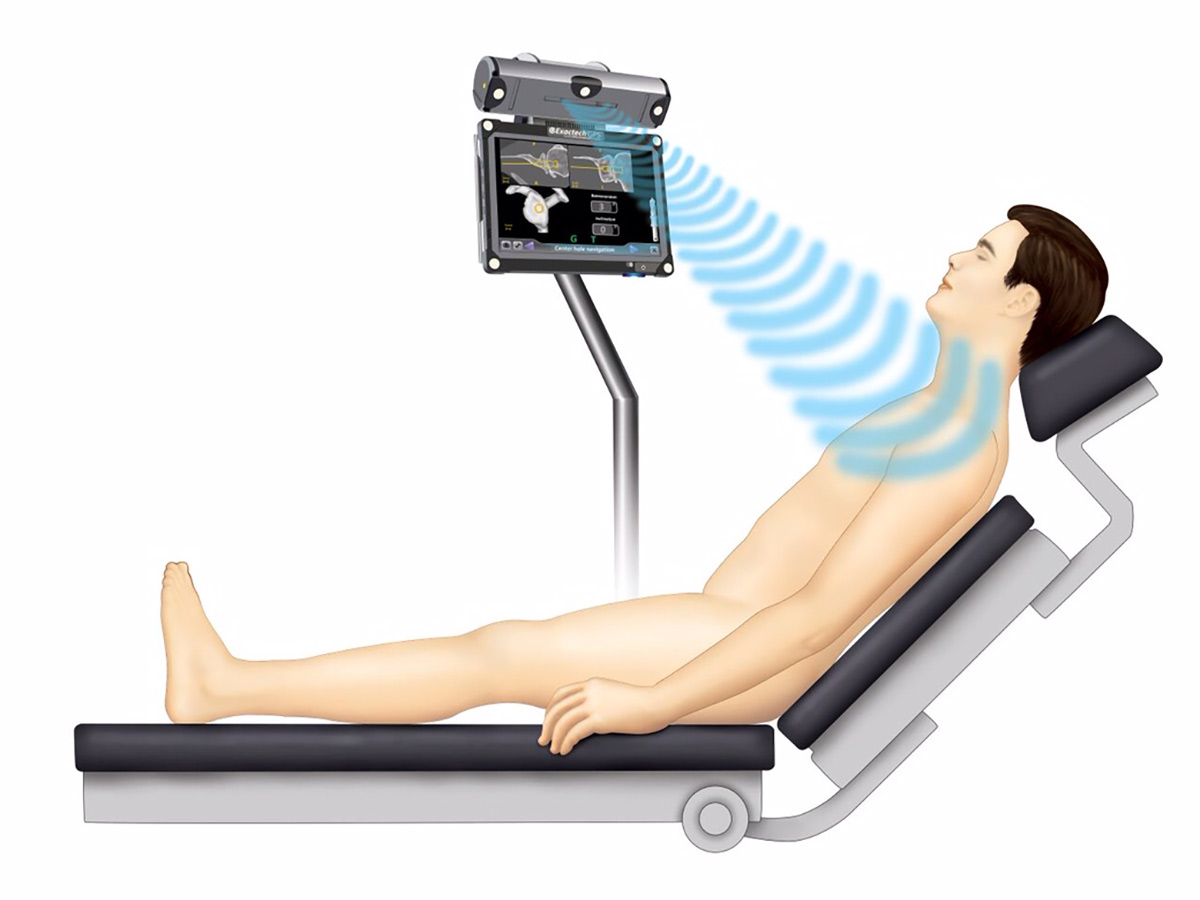
(full or partial joint replacement, axis led implants) incl. computer assisted navigation (Orthopilot) and minimal invasive techniques.
less soft tissue trauma
lower blood loss
faster recovery and rehabilitation
Orthopilot:
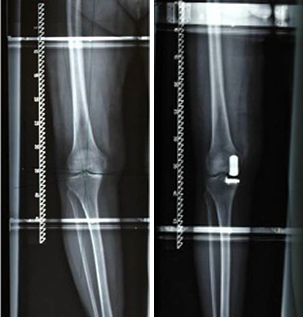
Partial joint replacement
Status pre and post-op
Full joint replacement
Status pre and post-op
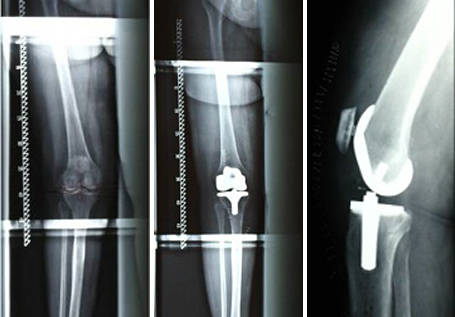
Revision operations of knee joints (loosenings, inflammations, implant failure)
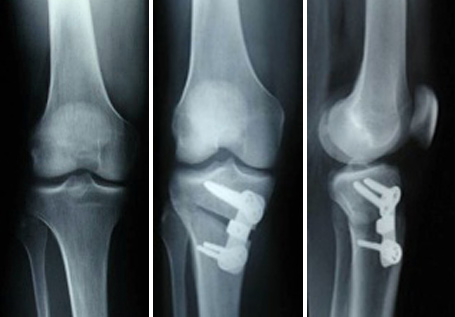
Axis corrections on thigh and lower leg for bowleg (genu varum) or knock-knee (genu valgum)
Status pre and post-op
Minimal invasive knee surgery (arthroscopy):
Meniscus injury or rupture of the cruciate ligament can be corrected without an essential opening of the joint.
The advantages of arthroscopy are a short hospital stay and a fast rehabilitation.
Ankle joint and foot
Upper ankle joint arthrosis:
Replacement by an artificial joint to keep the remaining mobility, or stiffening.
Arthrosis of the lower ankle joint
or severe malpositions of the foot (pes valgus / flatfoot) requiring bone and/or soft tissue corrective interventions.
Hallux valgus and hammertoes:
Numerous surgical techniques exist for the correction of malpositions of the toes.
Most important is to know the reason for the malposition, to select the most appropriate method.
Treatments for calcaneal spur, achilles tendon seam, removing ganglions
Shoulder and arm complaints
As a consequence of wear and accidents,
from endoscopy all the way to shoulder prostheses:
Impingement syndrome:
The narrowing of the space between the humerus head and the acromion due to osseous formations or alterations in the rotator cuff causes unpleasant symptoms in specific movements (esp. if the arm is raised over the head) or when lying on the affected shoulder at night. These symptoms can be eliminated by interventions on the soft tissue or reducing the narrowing bone structures.
Tears of the rotator cuff:
Operative reconstruction of the main tendons of the rotator cuff in order to restore full mobility and arm strength.
Calcification:
Endoscopic or open removal of calcifications from the tendons of the rotator cuff.
Acromio-clavicular joint erosion:
Relief of the acromio-clavicular joint through ligament stabilisation or joint resection.
Dislocations of the shoulder joint:
Endoscopic and open stabilisation of the shoulder in cases of shoulder luxation (both hereditary and due to an accident).
Erosion of the shoulder joint:
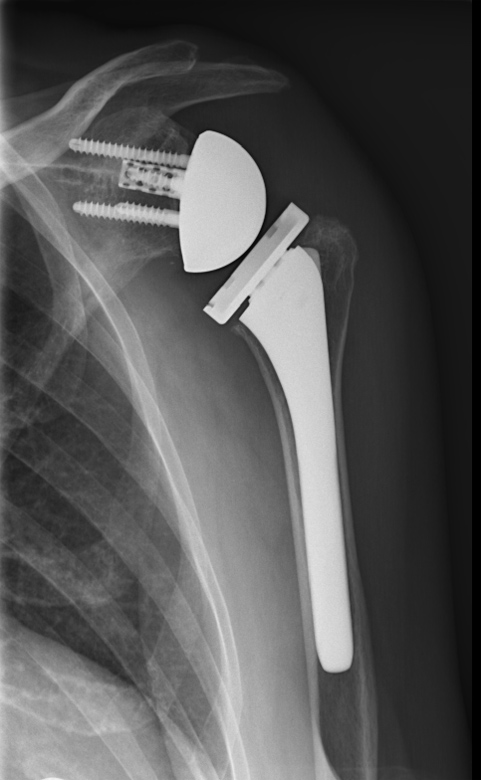
Implanting of (partial or total) shoulder prostheses, re-establishing conditions under which patients are pain-free and able to exercise normal force and functions of the shoulder joint. Even in hopeless cases with complete rupture of the rotator cuff and immobility of the arm as a result, mobility and fast pain relief can be achieved by a special so-called reverse shoulder prosthesis.
ORF-Beitrag “Bewusst Gesund” Inverse Schulterprothese
Neuer Meilenstein – 3D-Navigation
“Punktlandung bei Schulter-Operationen”
Moderne 3D-Navigation erhöht die Genauigkeit bei der Operation von Schulter-Gelenksprothesen auf nahezu 100%.
Patientenstory Alois Weingartshofer
„Endlich wieder einen Film zu Ende sehen!“
Als die Schulterschmerzen zu arg wurden, ließ sich Alois W. nach einer innovativen Hightech-Methode operieren. Seitdem erlebt er eine neue Dimension an Lebensqualität
3D-Navigation für Schulter-Gelenksprothesen-OP
Mit dem Exactech GPS System steht seit Anfang 2020 im Wiener Evangelischen Krankenhaus die neueste Methode der dreidimensionalen Navigation bei der Schulter-Endoprothese zur Verfügung.
Artikel in PDF >>
Wenn Haarekämmen endlich nicht mehr wehtut
Für viele – vor allem ältere Menschen – wird der Schulterschmerz im Alltag bereits zu Qual.
Artikel in PDF >>
Habe neue Lebensqualität
Starke Schulterschmerzen machten Alois Weingartshofer schwer zu schaffen.
Artikel in PDF >>
Hand
Signs of wear in hand and finger joints:
Surgical treatment with conservative measures (synovectomy – joint cleaning),
arthrodesis (fusion of joints) or endoprostheses (artificial joints).
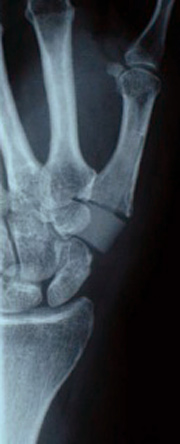
Saddle thumb joint osteoarthritis:
Worn out joints in the area of the thumb saddle joint are especially painful because many movements of everyday life are just possible with pain (i.e. opening a bottle, holding a pencil, wringing out a cloth, etc.). In this case, the implantation of a thumb joint “spacer” can very quickly restore function and power, without shortening of the thumb, which must be taken into account with other techniques.
Tendon corrections for:
Snapping fingers, torn tendons, inflammations of tendons or ganglia.
Trapped nerve syndromes (e.g. carpal tunnel syndrome):
Exposure and relief of the affected nerves and improvement through soft tissue release.
Deformities in hand and finger joints after accidents:
Bone fractures and lesions of the tendons sometimes result in restricted movement that is also painful; such restrictions to mobility can be improved or eliminated through surgical treatment of the bones, joints, ligaments and tendons.
Multiple deformities and fractures of the rheumatic hand
Artikel – Gesundheit Daumen “Das Daumensattelgelenk”

Post-op:
Implantation of a
thumb joint spacer